Foundations of the Future : Trying to get behind Research Papers That Changed the Game
Published:
CNNs ,RNNs and LSTM
| Paper | Link | Key Highlights | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
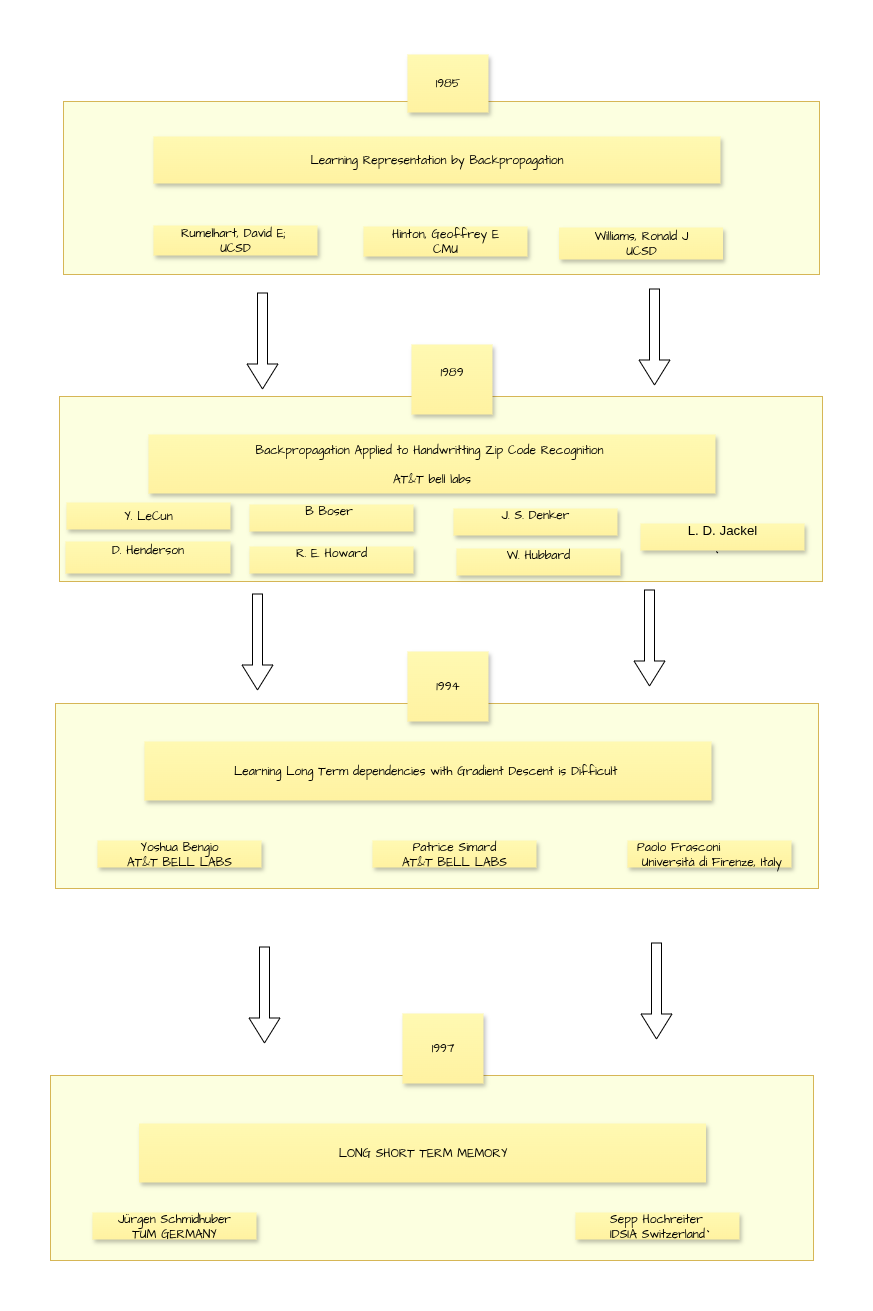
| Learning Representation by Backpropagation | • Introduced the backpropagation learning procedure for training multilayer neural networks, enabling them to learn internal representations and features essential for solving complex tasks unattainable by simple perceptrons. • Introduced momentum in gradient descent for acceleration and weight-decay regularization to improve generalization. • Demonstrated that multi-layer networks could successfully approximate complex nonlinear mappings. | 1985 | |
| Backpropagation Applied to Handwriting Zip Code Recognition | • Developed the convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture for image recognition, applying backpropagation to recognize handwritten ZIP codes from raw pixel input. • Showed CNNs could automatically learn relevant feature hierarchies (edges, shapes, etc.) directly from data without manual feature engineering. • Highlighted challenges in generalizing to out-of-distribution data and handling varied handwriting styles or noise. | 1989 | |
| Learning Long Term Dependencies with Gradient Descent is Difficult | • Analyzed why standard gradient descent methods (such as backpropagation-through-time) struggle to learn long-term dependencies in recurrent neural networks. • Identified the vanishing and exploding gradient problem, where error signals decay exponentially or grow uncontrollably. • Theorized with proofs and experiments that problems requiring retention of information over long intervals are essentially inaccessible to standard RNN training. | 1994 | |
| Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) | • Identified the vanishing/exploding gradient problem in RNNs. • Proposed the LSTM architecture. • Demonstrated experimentally that LSTM can bridge minimal time lags of hundreds or thousands of steps where previous methods fail. • Shown to have favorable complexity: O(1) per step/weight, similar to BPTT, and local in space and time. | 1997 |
MAML , Seq2Seq ,Transformers , BERT & GPT
| Paper | Core Goal | Key Idea / Architecture | Strengths | Limitations | Legacy / Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seq2Seq (2014) Sutskever, Vinyals, Le | End-to-end sequence mapping (e.g., machine translation). | Encoder–decoder LSTMs, with a “reverse source” trick to ease training. | First strong neural MT system, robust to long sentences, learned semantic sentence embeddings. | Bottleneck of fixed vector; vocab limits (UNK); data hungry; hard optimization. | Sparked neural MT revolution; laid groundwork for attention + Transformers. |
| Transformer (2017) Vaswani et al., “Attention Is All You Need” | Faster, more scalable sequence modeling. | Pure self-attention (no recurrence or conv), multi-head attention, positional encodings. | Parallelizable; better long-range modeling; SOTA in MT. | Quadratic self-attention cost; still compute heavy for long sequences. | Paradigm shift; foundation of modern NLP, vision, multimodal models. |
| GPT (2018) Radford et al., “Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training” | Universal transfer for NLP tasks. | Two-stage: pre-train on LM objective (unidirectional) → fine-tune via task serialization. | Strong transfer; simple traversal-style input; SOTA on many NLP tasks. | Unidirectional context; task mismatch risks; smaller scale vs successors. | Pioneered pre-train → fine-tune pipeline; ancestor of GPT-2/3/4. |
| BERT (2018) Devlin et al. | Deep bidirectional pre-training for language understanding. | Transformer encoder with MLM + NSP; fine-tune for downstream tasks. | Huge SOTA gains on GLUE, SQuAD, etc.; bidirectional context; versatile with minimal task tweaks. | [MASK] mismatch; fine-tuning instability; heavy compute cost. | “ImageNet moment” for NLP; inspired RoBERTa, ALBERT, DistilBERT, and more. |
| MAML (2017) Finn et al. | Meta-learning for fast adaptation to new tasks. | Inner loop (task adaptation) + outer loop (meta-optimization) to learn good initial weights. | Few-shot learning success; general framework (works for vision, RL, etc.). | Expensive (2nd-order gradients); sensitive to task distribution + hyperparams. | Landmark in meta-learning; inspired FOMAML, Reptile, ANIL, etc. |
| MultiModel (2017) Kaiser et al. | Unified multitask, multimodal learning. | Shared Transformer-style core + modality-specific subnets for text, vision, speech. | First real multimodal generalist; showed surprising cross-domain transfer. | Lagged behind top specialist models; very resource heavy; complex to train. | Early blueprint for generalist AI; influenced multimodal transformers (PaLM-E, Flamingo, GPT-4V). |
